We are no strangers to the well-known negative impacts of beer consumption. However, there is a plethora of positive information regarding the effects of beer on the body. So, is drinking beer good for you? Let’s delve into this topic with Kamereo in the following article!

Table of Contents
- Nutritional Components in Beer
- Is Drinking Beer Good for You?
- Is drinking a lot of beer good? How harmful?
- Frequently Asked Questions about ‘Is Drinking Beer Good for You”
Nutritional Components in Beer
According to nutritional charts, beer often contains empty calories but provides small amounts of minerals and vitamins such as potassium, calcium, thiamine, iron, and zinc. Therefore, to meet daily nutritional needs, you would need to consume a large amount of beer, which is not recommended.
Additionally, the vitamin B content, along with minerals in beer, is a result of the grains and yeast used in the production process. Light beers, with about 2/3 fewer calories than regular beer and slightly less alcohol, are available. While beer provides some essential nutrients, it cannot replace whole foods like fruits and vegetables.

Is Drinking Beer Good for You?
Scientific studies indicate that consuming beer in low amounts offers some health benefits. However, excessive intake can lead to severe health consequences. To understand the effects of drinking beer, let’s explore the content below.
Cardiovascular Health Support
According to the statistics from the Ministry of Health, approximately 200,000 deaths occur annually due to cardiovascular diseases, accounting for 33% of total deaths. Therefore, safeguarding cardiovascular health is crucial. A 12-week study on overweight adults revealed that moderate beer consumption (one glass per day for women and two glasses per day for men) could improve the antioxidant properties of HDL cholesterol (beneficial fat) and increase the removal of bad cholesterol from the body.
Another review suggested that moderate beer consumption might reduce the risk of heart disease, similar to red wine. However, these benefits apply only to moderate consumption; excessive alcohol intake may increase the risk of heart disease and stroke.
Insulin Control
Moderate alcohol consumption, including beer, may contribute to better blood sugar control, a common concern for individuals with diabetes. Numerous studies have shown that moderate alcohol consumption can reduce insulin resistance, a risk factor for type 2 diabetes. In a large study with over 70,500 participants, moderate alcohol consumption was associated with a 43% reduction in diabetes risk in men and a 58% reduction in women.
Bone Health Support
Certain types of beer contain orthosilicic acid (OSA), contributing to bone density and improving bone health. Beer also contains specific minerals supporting bone formation and protection. However, excessive beer consumption may have negative effects on the body. While beer can contribute positively to bone health, it’s essential to note that minerals in beer are not exceptionally high, and other healthy foods can be consumed for the same benefits.
Memory Improvement
The benefits of moderate beer consumption may reduce the risk of memory-related issues. However, it’s crucial to emphasize that excessive alcohol consumption may increase the risk of cognitive decline.
Is drinking a lot of beer good? How harmful?
Drinking beer is beneficial for health only when done in moderation. For men, the recommended limit is 2 cans per day, and for women, it is 1 can per day. Prolonged and excessive alcohol intake can significantly impact health in various ways:
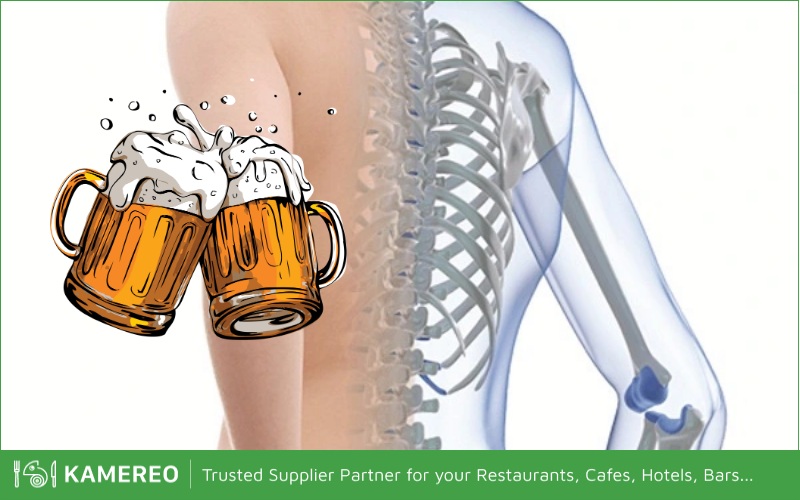
Serious Impact on the Liver
The liver struggles to efficiently metabolize the alcohol in beer, leading to damage and reduced ability to filter harmful toxins from the blood. Excessive beer consumption is a major cause of liver cirrhosis, a condition characterized by increased swelling and damage to the liver due to the accumulation of fibrous tissue.
Damage to the Stomach Lining
Whether one should drink beer depends on individual needs, but moderation is crucial. Beer can erode the protective mucus layer of the stomach lining. Moreover, consuming excessive amounts of these beverages can elevate stomach acid levels, directly affecting the stomach lining, resulting in inflammation, ulcers, and symptoms like belching, acid reflux, and discomfort.
Impact on the Nervous System
The alcohol in beer can affect the brain, impeding the transmission of signals within the nervous system. This can lead to delayed reflexes, mood changes, and loss of balance. Additionally, excessive beer consumption may cause the shrinkage of brain cells, contributing to cognitive impairment and memory disorders.

Increased Cancer Risk
Similar to tobacco, excessive beer consumption is a risk factor for various cancers. Statistics indicate that cancers such as throat, colon, mouth, and liver cancer are often associated with excessive beer consumption. Beer also enhances the absorption of cancer-causing substances in cigarettes, generating highly active molecules that damage DNA.
Urinary Disorders
Beer is a potent diuretic, and excessive daily consumption increases the workload on the kidneys, causing problems such as frequent urination, painful urination, and nighttime urination. Moreover, beer acts as a powerful nerve suppressant, inhibiting the urinary process and leading to an increased risk of acute urinary retention and associated damage.

Immune System Suppression
Studies on regular beer drinkers have shown decreased white blood cell counts, primarily due to the prolonged impact of alcohol on these cells. This results in compromised immune defenses and a weakened natural immune system. Consequently, those who frequently consume alcohol are more susceptible to various illnesses.
Hormonal Imbalances
Excessive beer consumption can directly impact hormonal balance. For women, it may lead to shortened menstrual cycles, affecting the formation and development of the fetus. In men, it can cause erectile dysfunction, reduced sperm concentration, and testicular atrophy.

Osteoporosis Risk
While moderate beer consumption can contribute positively to bone health, excessive beer intake can negatively affect the formation of new bone, decrease calcium levels, and lead to conditions like osteoporosis and brittle bones.
Frequently Asked Questions about ‘Is Drinking Beer Good for You”
After exploring the content above, you may have gained some insights into whether drinking beer is beneficial for health. Here are some of the most common questions and answers regarding the potential benefits and drawbacks of consuming beer.
Is Drinking One Beer a Day Good for You?
Drinking one beer a day, especially within the recommended limits (one for women and two for men), can offer certain health benefits. However, excessive beer consumption, particularly getting intoxicated, may lead to health issues such as an increased risk of liver disease, cancer, and osteoporosis.

When Is the Best Time to Drink Beer?
The ideal time to consume beer is before or during a meal. A beer can stimulate digestion, enhance appetite, and provide a pleasurable experience. Additionally, having a beer in the evening can help with relaxation and stress relief after a long day. Avoiding late-night beer consumption is advisable to prevent sleep disturbances and nighttime urination.
How Should Beer Be Consumed for Optimal Benefits?
Dr. Truong Dinh Bac, Deputy Director of Preventive Health, Ministry of Health, recommends moderate beer consumption to avoid exerting excessive pressure on the liver. It is advised not to exceed two 330ml cans of beer per day for men and one for women. Consuming large quantities in one sitting may pose health risks. Choosing reputable beer brands is also essential to minimize the risk of poisoning.

Who Should Avoid Beer Consumption?
Certain individuals are advised to refrain from consuming beer, including pregnant women, children, individuals with heart issues, those experiencing depression, individuals with liver and pancreatic diseases, and those engaged in precision-demanding occupations. These precautions aim to prevent potential negative impacts on health and well-being.
Can Beer Help with Weight Loss?
Despite having empty calories, the alcohol in beer is not conducive to weight control or loss. If following a healthy diet, it is recommended to reduce beer intake, as excessive consumption can contribute to weight gain.

What Happens If You Consume Expired Beer?
Drinking expired beer can lead to food poisoning, causing symptoms such as abdominal pain, diarrhea, vomiting, and fever. Expired beer may also pose difficulties in digestion.
Is It Better to Drink Beer with or without Ice?
Drinking beer without ice is generally considered better for health. Cold temperatures can cause throat inflammation and potentially affect digestion. Whether with or without ice, moderation is key.

Read more: How many calories in unsalted butter? Is unsalted butter fatty?
Hopefully this article will help you partly answer the question of whether drinking beer is good or not. Although there are many records about the effects of drinking beer, you should only consume it in moderation. In particular, you should not drive after using alcohol to ensure safety for yourself and everyone. Don’t forget to follow the Health & Beauty section for more useful information!